EASE OF USE
LEO is the only training system that fits in an airplane cabin baggage, it weights less than 10 kilograms. Set up your training center in less than two minutes and store it in a cabinet when you are done
Read moreEFFECTIVE TRAINING
LEO is the only system that faithfully reproduces the look and feel of the robot console. Its accurate simulations ensure an effective training and save trainee’s and supervisor’s precious time
Read moreCLOUD DATA ACCESS
LEO stores training data in the Cloud. Thus users can track their progresses with ease and supervisor can analyze and evaluate user’s skill imrpovement over time from any platform.
Read moreLEO CONSOLE
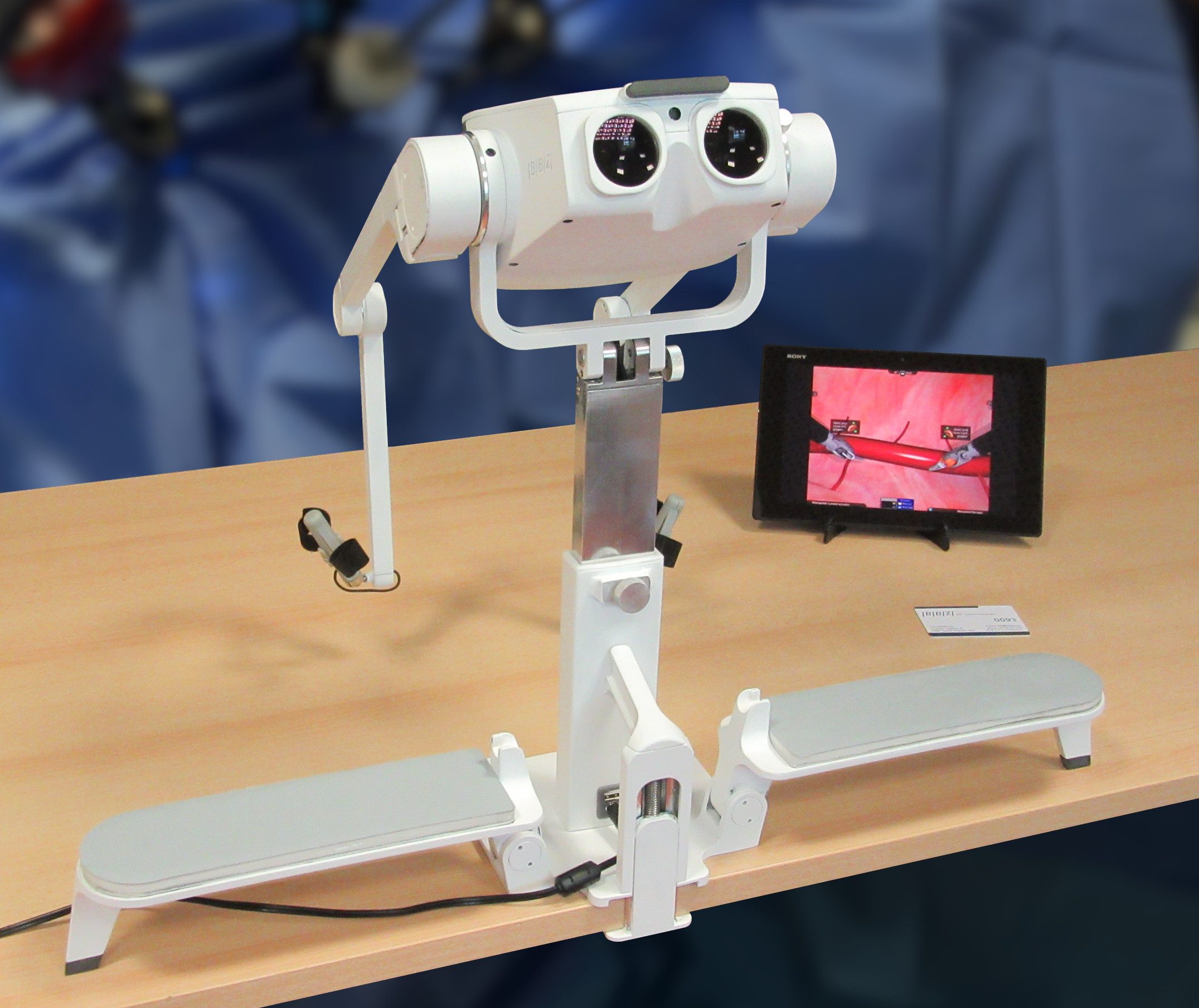
Portable and lightweight
LEO console is unique: it is the only console designed from scratch to accurately reproduce the user experience of the real robotic console.
It provides the highest graphics resolution on the market and it is the only one that mimics the inertia of robot console arms.
Thanks to its foldable design the console and the pedal tray fit in a cabin baggage and deploy in less than two minutes.

LEO SOFTWARE
Realistic and effective simulations
LEO ensures realistic and accurate training scenarios. This is important to shorten trainee learning curve and to ensure the quality of the training.
With more than 30 tasks in 8 categories trainee acquires all the skills required to effectively control the surgical robot.
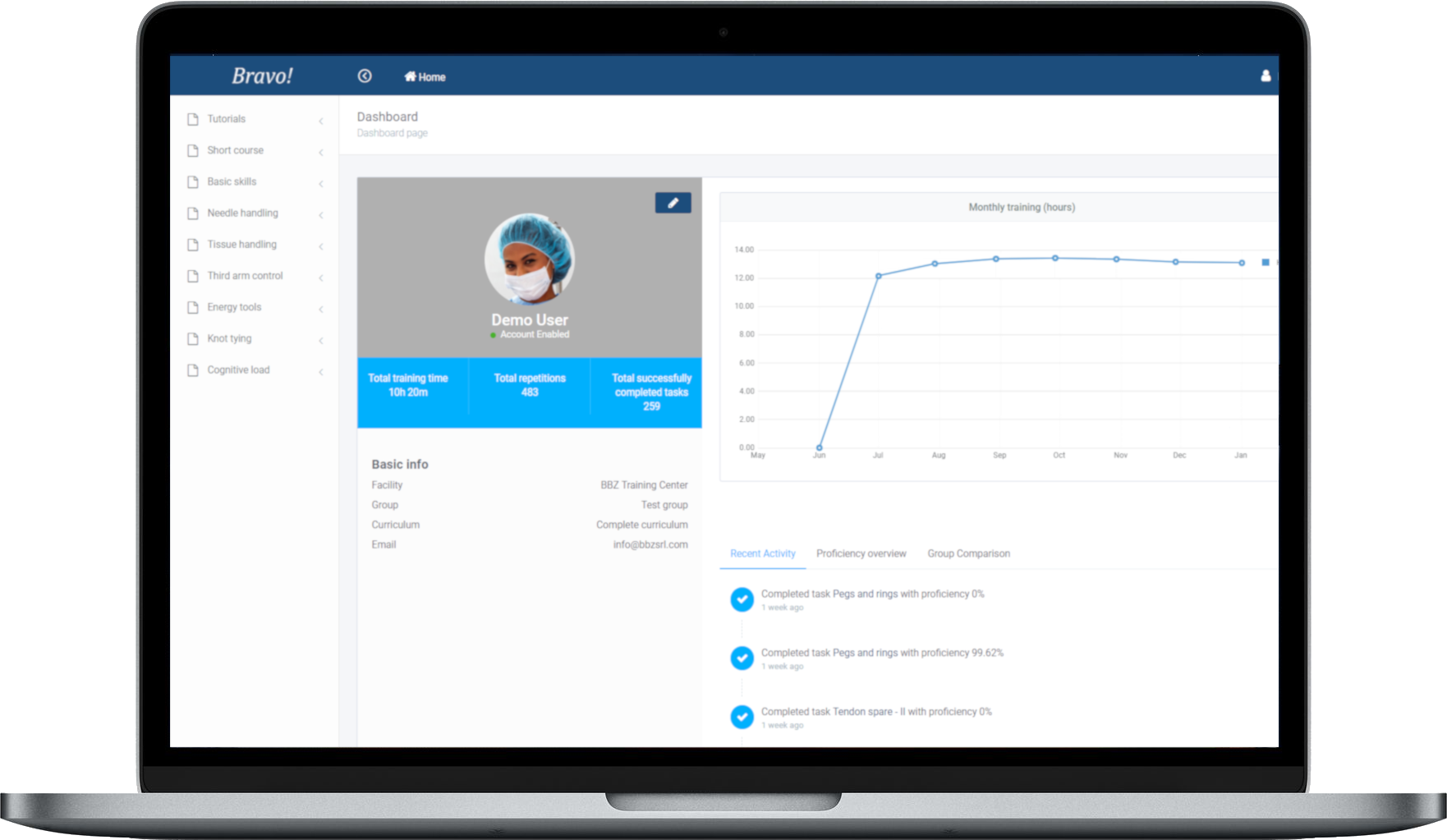
CLOUD DATA ACCES
Access training data anywhere
Trainees access LEO via a personal badge and LEO saves all their training data on Bravo!, BBZ proprietary cloud system.
On Bravo! trainees track their training outcome from their phone or computer while training supervisor can follow results for single users or groups.
All data can be downloaded in Excel format for further analysys.
Publications
G. Menegozzo; D. Dall’Alba; C. Zandonà; P. Fiorini: Surgical Gesture and Error Recognition with Time Delay Neural Network on Kinematic Data. Proceedings of the 9th Joint Workshop on New Technologies for Computer/Robot Assisted Surgery, pp. 60-62, 2019
G. Menegozzo; D. Dall’Alba; A. Roberti; P. Fiorini: Automatic process modeling with time delay neural network based on low-level data. Procedia Manufacturing, 38 , pp. 125–132, 2019.
T. Haruki; H. Nakamura: Surgical simulation in robot-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: future strategy. Video-assist Thorac Surg 2018;3:44.
F. Bovo; G. De Rossi; F. Visentin: Surgical robot simulation with BBZ console. The Journal of Visualized Surgery (JOVS) Vol 3:4 2017
D. Zerbato; D. Dall’Alba: Role of virtual simulation in surgical training. The Journal of Visualized Surgery (JOVS) Vol.3:3 2017
G. Borghini; P. Aricò; G. Di Flumeri; A. Colosimo; D. Zerbato; F. Bovo; S. Storti; G. Menegaz; P. Fiorini; F. Babiloni: Neurophysiological metric for the objective training assessment of user during simulated robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery. 34th annual international conference f the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC 2016)
D. Zerbato; L. Bertelli; F. Bovo; V. Cantù: Training for surgical knot tying with knot recognition and thread snapping. Computer assisted robotics and surgery (CARS 2015)
D. Zerbato: Accurate and cost-effective trainer for robotic surgery. The Hamlyn symposium workshop on cognitive surgical robotics 2014
J. A. Sánchez Margallo; J. B. Pagador; L. F. Sánchez Peralta; J. L. Moyano Cuevas; L. Gasperotti; D. Zerbato; L. Vezzaro; F. M. Sánchez Margallo: A preliminary validation of the Xron surgical simulator for robotic surgery. 25th International Conference of the Society for Medical Innovation and Technology (SMIT 2013)
Some users of LEO



Contact us
If you want more information or for a quotation

